Sales is a common term when it comes to business. If someone asks you, “What is sales?” you probably would say it means selling a product or service to a consumer or business. But, in reality, it means a lot more than that.
Whether you are a seasoned professional looking to hone your skills or a curious newcomer looking to understand this crucial field better, we will discover what sales are all about in this article.
To boost sales, small business owners may need expert assistance with generating new leads, improving branding, or growing their online presence. This is where BrandLoom can be a great asset.
What is sales? Sales Meaning in Business.
Sales is the complex relationship between two or more parties that involves communication, persuasion, and building relationships to drive transactions and allow the exchange of goods, services, or ideas.
Understanding customers’ wants, giving them custom solutions, and earning their trust are all important parts of the process.
Sales matter when it comes to making money and growing a business. It is important to balance meeting customers’ needs and moving the company’s mission forward. To keep a business going, you need to find new customers and keep the ones you already have happy and loyal.
If you want to know what is sales all about, then remember that the world of sales is both diverse and complicated. It includes business-to-business (B2B), retail, service industries, and online shopping.
Businesses use different selling methods to keep up with changing customer tastes and market conditions. The methods can be different, like consultative selling, which focuses on finding and getting rid of customer pain, or solution selling, which positions products as solutions to specific problems.
Modern strategies incorporate data analytics, customer relationship management (CRM) software, and other automation software to keep up with the ever-changing digital landscape.
Despite these advances, however, the importance of the human touch cannot be overstated. Successful sales results continue to be driven by genuine interactions and genuine relationships.
In the following posts, we will examine the finer points to discuss industry best practices, and provide concrete examples to illustrate the science and art of selling.
Sale Definition
A sale is the act of selling a product or service in exchange for money or other compensation. It is an activity that forms part of commerce. A sale is completed when the buyer agrees to the terms and provides the required compensation, at which point ownership of the goods or services is transferred from the seller to the buyer.
Sales Definition: What is Sales Definition
Sales refers to the activities related to selling or the number of goods or services sold in a given time period. The term encompasses the entire process of promoting and selling goods or services to customers, including marketing, lead generation, negotiation, and closing deals. Sales can also denote the revenue or volume of sold goods or services. In organizational setups, the term often refers to a division or department dedicated to these selling activities.
Sale vs. Sales
Both “sale” and “sales” pertain to the act of selling, but they are used in slightly different contexts:
Sale:
- Singular noun.
- Refers to a single transaction in which goods or services are transferred from the seller to the buyer in exchange for money or other compensation.
- Can also refer to a special promotion or event where goods are offered at reduced prices: “There’s a big sale at the mall this weekend.”
Sales
- Plural noun.
- Refers to the total number of goods or services sold over a specific time period or in total: “The company reported an increase in quarterly sales.”
- Can also refer to the department or team responsible for selling a company’s products or services: “She works in sales.”
- Additionally, “sales” can denote the act or process of selling products or services: “She’s excellent at sales.”
In a nutshell, “sale” often refers to a single transaction or promotional event, while “sales” often refers to the cumulative number of transactions, the process of selling, or the department responsible for selling.
Example of sales – A step-by-step approach
Let’s take a look at an example of a scenario and sales information to better understand how the process works:
Selling High-End Fitness Trackers
Imagine selling fitness trackers. You want to sell these fitness trackers to tech-savvy, health-conscious people.
- Prospecting: Find customers. Find people discussing fitness goals and tracking methods on forums, social media, and fitness events.
- Initial Contact: You send personalized emails or messages after identifying potential leads. Introduce yourself and your product, highlighting its heart rate monitoring, GPS tracking, and compatibility with popular fitness apps.
- Needs Assessment: When talking to potential customers, you ask about their fitness goals and pain points. One prospect is training for a marathon and wants a device to track and improve their running performance.
- Presenting Solutions: Tailor your pitch to the prospect’s needs. Focus on the fitness tracker’s marathon training features, such as accurate GPS tracking, real-time performance data, and personalized training plans.
- Addressing Objection: The prospect is concerned about the fitness tracker’s price. You counter this objection by emphasizing the device’s long-term health and training benefits. You also mention promotions and financing.
- Negotiation and Closing: After addressing objections and providing additional information, you present a limited-time offer with a discounted price, a free fitness consultation, and a personalized training plan. The prospect buys after hearing the value proposition.
- Follow-Up: After the sale, you check customer satisfaction. You help set up the device, sync it with their smartphone, and answer questions.
This example involves understanding the customer’s needs, tailoring the pitch, and building a relationship beyond the transaction. Sales require good communication, product knowledge, and value creation.
Importance of sales
If you want to learn what sales is useful for, then check out the points given below:
Revenue Generation:
Revenue and sales are closely related. It is the cash that customers give the company in exchange for goods or services. Without income, a business cannot pay its bills, pay its workers, invest in expansion, or even stay afloat. Revenue provides financial support for all business activities.
Business Survival:
The survival of a business depends on sales. No matter how cutting-edge a product or service is, there would be no market or demand for it without successful strategies. It guarantees that a company will remain valuable, relevant, and competitive.
Market Expansion:
Successful sales enable companies to investigate new markets and clientele. This growth may be geographic, reaching out to new areas, or demographic, focusing on various customer types. By reducing reliance on a single market, customer base diversification lowers risk.
Employment Possibilities:
A successful sales department generates numerous job opportunities. To support the process, several positions outside of sales are required, including those in marketing, customer service, logistics, and production. The economy will grow as a result of this job creation.
Innovation and Research:
Sales interactions offer insightful information about customer preferences, behaviors, and new trends. Businesses can stay ahead of the curve by innovating and creating new products or services that cater to customer needs by understanding their wants and needs.
Marketing Alignment:
Marketing strategies are improved by effective feedback. It aids marketing teams in honing their messaging, determining their target markets, and customizing campaigns to reach prospective clients more. This alignment ensures the conversion of marketing efforts into fruitful leads.
Customer Relationships:
When interacting with customers personally, salespeople serve as the company’s public face. These connections are based on mutual understanding, meeting customer needs, and trust. Strong connections result in repeat business, customer loyalty, and favorable word-of-mouth recommendations.
Brand Visibility:
Sales efforts introduce Potential customers to a company’s goods or services. Successful marketing initiatives increase brand recognition and visibility, improving brand recall in consumers’ minds.
Competition and Innovation:
Competition pushes companies to improve. Companies innovate to outperform competitors, enhancing customer experiences.
Economic Growth:
Businesses boost economic growth by selling goods and services. Economic activity generates taxes, jobs, and consumer spending.
Partnerships and Alliances:
Sales can lead to business partnerships. These alliances allow companies to share strengths, expand their reach, and offer complementary products or services.
Feedback Loop:
Sales interactions provide a valuable feedback loop. Experts ask customers about product performance, satisfaction, and improvement. Feedback refines and develops products and services.
Company Culture:
An ethical, customer-focused culture can impact the entire company. Customer-centricity encourages collaboration, innovation, and value delivery.
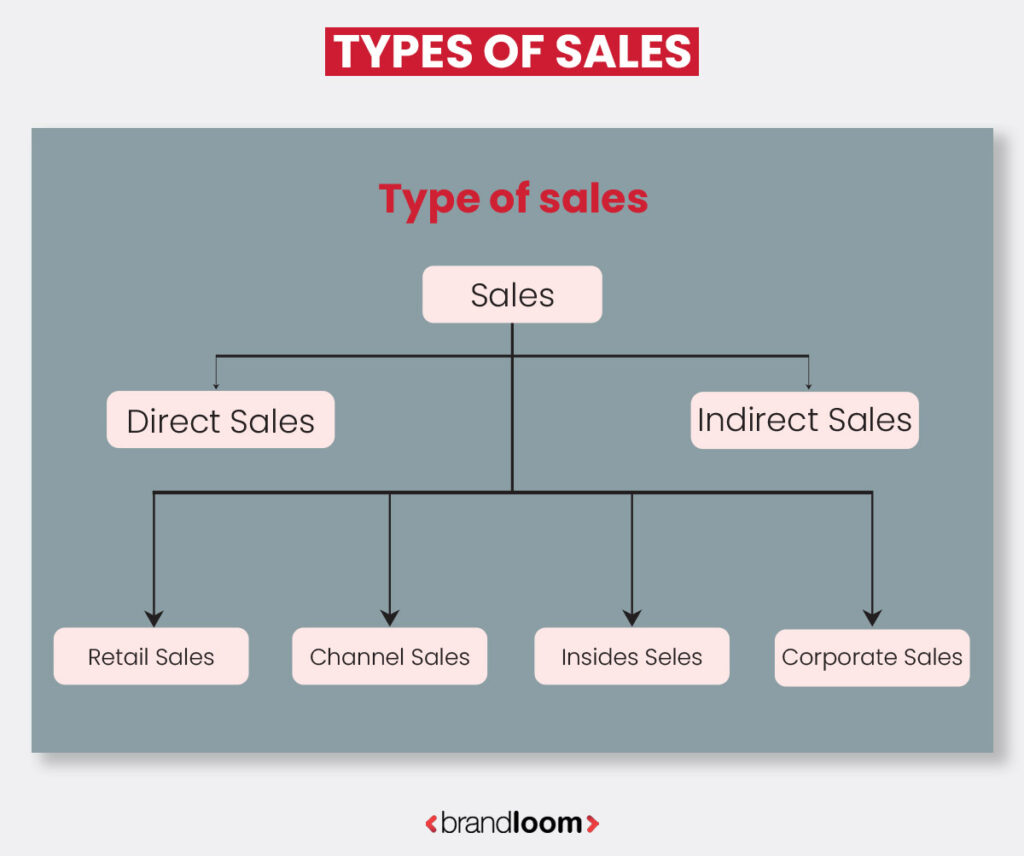
Types of Sales
Sales is a dynamic field with many ways to connect with customers and encourage transactions. These serve various industries, customer segments, and market conditions. We will examine some of the most common sales types, each with its traits and uses.
Retail Sales:
Retail ones are conducted in-person or online. Whether it is a brick-and-mortar store or an e-commerce site, retail ones focus on selling products to individual customers. These require product knowledge, customer service, and guidance through the buying process.
Business-to-Business (B2B) Sales:
B2B sales involve businesses selling to businesses. These cycles are longer and more complicated. B2B salespeople must understand the purchasing business’s needs, build relationships with key decision-makers, and negotiate to meet the business’s goals.
Business-to-Consumer (B2C) Sales:
B2C sales are transactions where businesses sell their products or services directly to individual consumers. These reach many people through various marketing channels. B2C sales may require engaging advertising, seamless online purchasing, and optimized user experiences.
Direct Sales:
Direct sales to consumers are made without a storefront. Door-to-door, in-home product demonstrations, and network marketing are examples.
Online Sales:
This occurs on websites or e-commerce platforms. User experience optimization, digital marketing, and online techniques are needed.
Channel Sales:
Distributors, retailers, and partners make channel sales. Distribution networks can help companies reach new markets with these sales strategies.
Transactional Sales:
Transactional sales are quick, one-time sales. This type of sale is typical for low-priced, frequently purchased items. Deals are closed quickly and efficiently.
Cross-selling and Upselling:
Cross-selling involves selling related products or services to an existing customer, while upselling involves persuading a customer to buy a higher-priced version of a product or additional features. These strategies aim to increase the average transaction value.
What is a sales funnel?
Have you ever wondered what a sales funnel is?
A sales funnel, also called a purchase funnel or conversion funnel, shows the customer’s journey from awareness to purchase. It shows how customers find a solution and buy. But what is a sales funnel useful for? These funnels optimize conversion paths.
The funnel typically consists of several stages, each representing a different phase of the customer’s progression:
Awareness:
Potential customers discover a product or service at the top of the funnel. Social media, advertising, content, and word-of-mouth can do this.
Interest:
Prospects show interest in learning more at this stage. They may visit a website or read blog posts, videos, or whitepapers.
Consideration:
As they move down the funnel, prospects evaluate whether the product or service meets their needs. They research, compare, and decide.
Intent:
Customers are ready to buy at this point. They may request a demo, sign up for a free trial, or add items to their e-commerce cart.
Evaluation and Decision:
Prospects compare benefits, features, and prices. Before deciding, they may consult salespeople and customer support or gather more information.
Purchase:
At the bottom of the funnel, prospects become customers by buying. Purchases, subscriptions, and contracts are examples.
Post-Purchase:
After making a purchase, customers enter the post-purchase stage. Businesses aim to provide excellent customer service, address concerns, and ensure a positive experience. Customer loyalty, referrals, and upselling/cross-selling opportunities can result.
What is the sales process?
Salespeople use a structured process to guide prospects from awareness to purchase. It is the backbone of all successful interactions, relationships, and sales. The following is a general outline of the typical process, which may vary depending on the industry, product, and strategy.
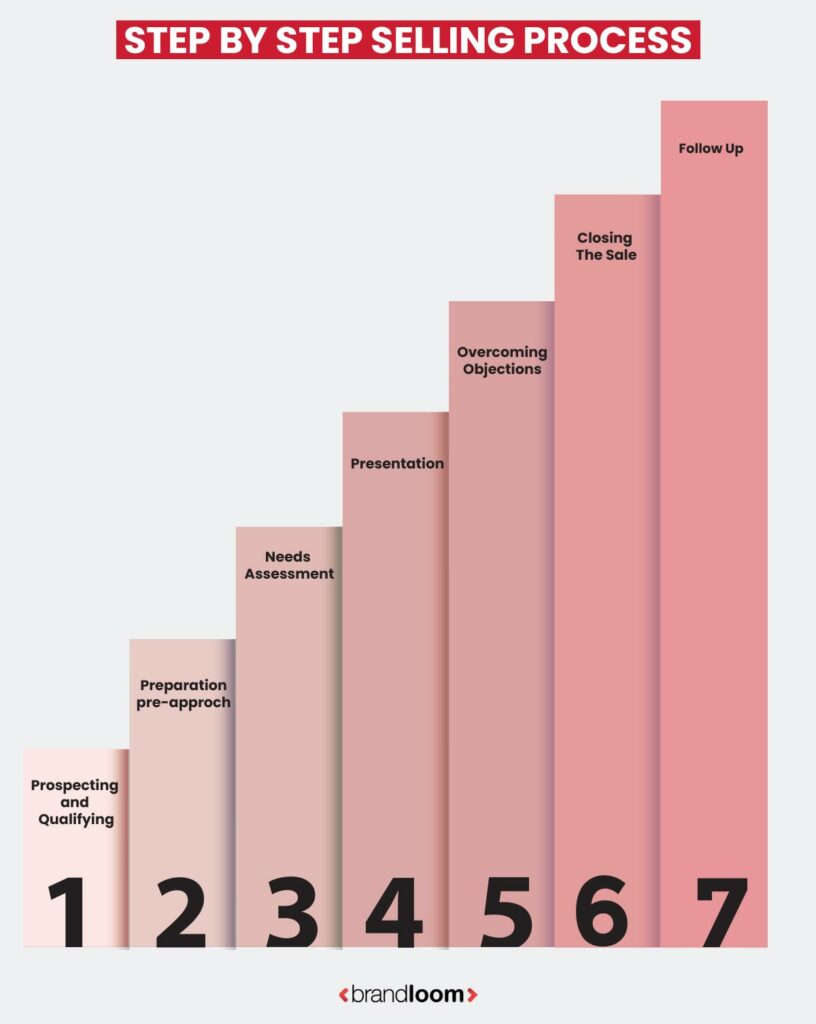
Prospecting:
This phase involves finding potential leads or prospects for your product or service. Prospecting methods include online research, networking events, social media, and customer databases.
Qualification:
Marketing professionals evaluate potential leads to determine whether they fit the product or service well. This involves assessing the prospect’s budget, timeline, needs, and decision-making authority.
Needs Assessment:
Sales experts talk to qualified leads about their problems. This step is crucial for tailoring your approach and presenting relevant solutions.
Presentation:
In this phase, you present your product or service to the prospect, emphasizing its value and suitability. This may involve demonstrating features and explaining benefits.
Handling Objections:
Prospects may have concerns or objections about your offering. Trained professionals overcome objections by providing more information, dispelling myths, and showing how your product or service solves problems.
Proposal and Quote:
After addressing objections and tailoring your pitch, you present a formal proposal with terms, pricing, and benefits. The prospect’s needs may dictate this step.
Closing:
The closing stage is when the prospect decides to purchase. It involves finalizing sales details, getting approvals, and ensuring the prospect is confident in their decision.
Follow-Up:
To ensure customer satisfaction, follow up after the sale. This step shows customer success and sets the stage for repeat business and referrals.
Customer Relationship Management:
Long-term relationships keep and grow customers. This requires regular communication, excellent customer service, and support.
Upselling and Cross-Selling:
Salespeople can maximize value by upselling or cross-selling as customers’ needs change.
Referrals and Testimonials:
Satisfied customers can become advocates for your brand by providing referrals and testimonials. This can help expand your customer base and build credibility.
Continuous Improvement:
Successful teams analyze their performance and outcomes regularly. They assess what’s working and what can be improved, refining their strategies and techniques.
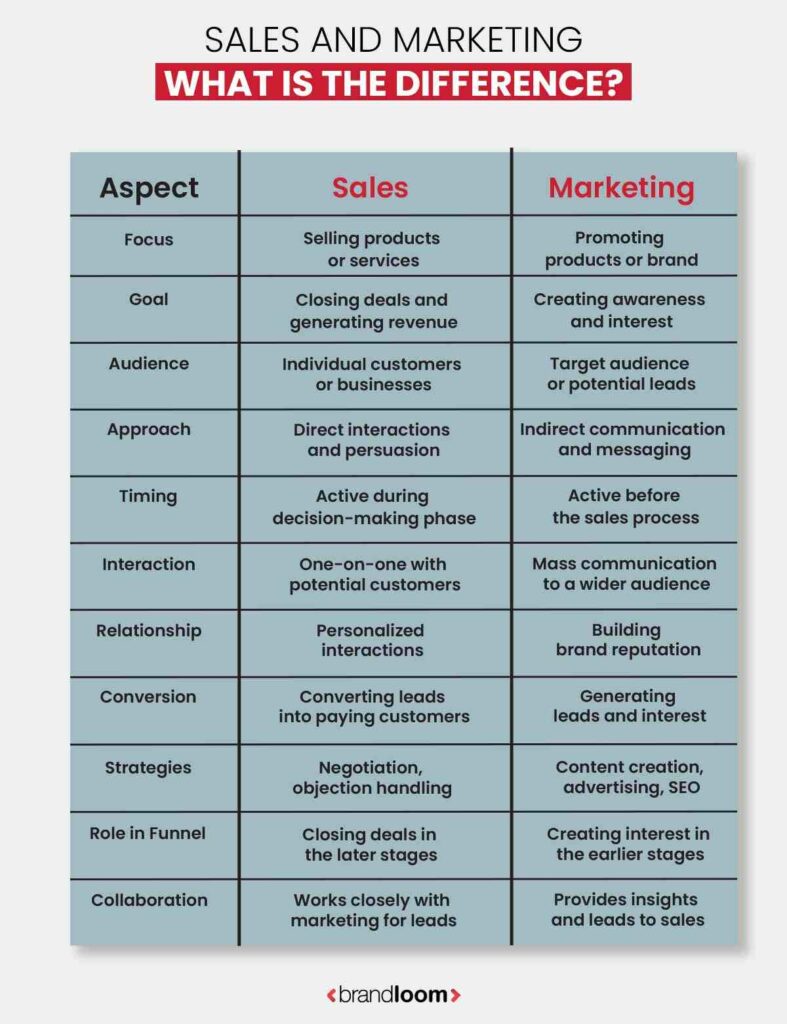
Sales and Marketing – What is the difference?
| Aspect | Sales | Marketing |
| Focus | Selling products or services | Promoting products or brand |
| Goal | Closing deals and generating revenue | Creating awareness and interest |
| Audience | Individual customers or businesses | Target audience or potential leads |
| Approach | Direct interactions and persuasion | Indirect communication and messaging |
| Timing | Active during decision-making phase | Active before the sales process |
| Interaction | One-on-one with potential customers | Mass communication to a wider audience |
| Relationship | Personalized interactions | Building brand reputation |
| Conversion | Converting leads into paying customers | Generating leads and interest |
| Strategies | Negotiation, objection handling | Content creation, advertising, SEO |
| Role in Funnel | Closing deals in the later stages | Creating interest in the earlier stages |
| Collaboration | Works closely with marketing for leads | Provides insights and leads to sales |
| Outcome | Direct revenue generation | Building a brand presence |
Role Marketing Plays in Sales and Sales Funnel
Marketing is an extremely important component in the sales process and funnel. It generates brand awareness through advertising and content marketing, which initiates customer engagement.
Marketing involves delivering persuasive information about a product or service to potential customers at various customer journey stages, such as interest and consideration. It helps build intent by highlighting offers and benefits, making evaluation easier through reviews and comparisons, and ensuring the purchase process goes smoothly overall.
Following a customer’s purchase, marketing will work to maintain their relationship with the company through various follow-ups and loyalty programs. In essence, marketing’s strategic integration at each stage enhances customer acquisition, retention, and overall business growth.
Conclusion
Sales is the dynamic and strategic process of connecting products or services with the needs and desires of potential customers.
It’s not merely about transactions; it’s about building relationships, understanding customer pain points, and presenting solutions that create value.
From prospecting and pitching to negotiating and closing, sales professionals navigate a multifaceted journey that requires a blend of interpersonal skills, product knowledge, and adaptability.
BrandLoom is one such platform that can help your sales grow in the least time possible. Successful sales efforts in today’s competitive landscape go beyond persuasion; they prioritize empathy, active listening, and a genuine commitment to meeting customer needs.
Ultimately, sales are the bridge that transforms curiosity into conviction and potential customers into satisfied, loyal advocates for a brand.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the definition of sales?
In a business context, sales refer to exchanging products, services, or ideas for monetary value or other forms of compensation.
It involves persuasive communication, relationship-building, and negotiation to convince potential customers to purchase.
Sales professionals aim to understand customer needs, present solutions that match those needs, address objections, and guide customers through decision-making, ultimately resulting in a successful transaction.
The goal of sales is to generate revenue, drive business growth, and foster customer relationships that lead to repeat business and referrals.2. What are the common types of sales?
There are several common types of sales, each catering to different industries, customer segments, and market dynamics. Here are some of the most prevalent types of sales:
Retail Sales: Sales of products directly to individual consumers in physical stores or online platforms.
Business-to-Business (B2B) Sales: Sales of products or services from one business to another business entity.
Business-to-Consumer (B2C) Sales: Sales of products or services directly to individual consumers.
Direct Sales: Selling products directly to consumers without using a retail location.
Online Sales: Sales conducted through e-commerce websites and digital platforms.
Channel Sales: Selling products through third-party intermediaries like distributors, retailers, or partners.
Transactional Sales: Quick sales of lower-priced products with a focus on efficiency.
Relationship Sales: Building long-term relationships with customers through trust and personalized service.
Inbound Sales: Responding to inquiries and leads generated by marketing efforts.
Outbound Sales: Proactively reach potential customers through cold calling or outreach.
Subscription Sales: Selling subscription-based services or products.
Each type of sales has its unique strategies, techniques, and challenges. Successful sales professionals understand how to adapt their approach to match the specific context and requirements of the sales type they are engaging in.3. What is the difference between B2B and B2C sales?
B2B (Business-to-Business) and B2C (Business-to-Consumer) sales differ in their target audience, complexity, decision-making, relationship-building, and marketing approaches.
Target Audience:
B2B: Targets other businesses, decision-makers, and procurement teams.
B2C: Targets individual consumers for personal use.
Sales Complexity:
B2B: More complex with longer sales cycles and specific business needs.
B2C: Simpler with shorter cycles based on personal preferences.
Decision-Making:
B2B: Involves multiple stakeholders and ROI assessment.
B2C: Driven by emotions and personal preferences.
Relationship Building:
B2B: Focuses on trust and long-term partnerships.
B2C: More transactional with brand interaction.4. How do sales and marketing relate to each other?
Sales and marketing are two closely related functions in a business, collaborating to drive revenue and business growth.
They share a common goal of attracting customers and increasing revenue. Marketing generates leads and nurtures them through the sales funnel, preparing them for interaction with the sales team.
Both teams align messaging to ensure consistency in communication and share insights about customer preferences. Sales provide direct customer feedback to marketing, influencing strategies.
The two functions collaborate through lead handoff, ensuring timely and personalized interactions. Integrated data systems help both teams track performance and make informed decisions. Ultimately, their synergy maximizes the effectiveness of the customer journey and contributes to overall business success.5. What is the purpose of a sales plan?
Sales plans organize and strategize sales goals. This comprehensive plan guides sales teams, managers, and the organization through the sales process. Sales plans give salespeople direction by setting goals, defining strategies and tactics, and allocating resources. It helps identify target markets, forecast performance, mitigate risks, and align sales and business goals objectives with the broader business goals. The sales plan facilitatemeasuring and evaluatingof sales activities and ensures adaptability to changing market conditions, fostering a proactive and coordinated approach to achieving sales success.
6. What is a sales pipeline?
Sales pipelines show how prospects become buyers. Sales teams use this framework to manage lead and prospect interactions. Leads, or potential customers, enter the pipeline early and advance as they demonstrate interest and engagement. This helps salespeople manage leads and resources. The pipeline’s visibility helps sales managers assess team performance, forecast sales revenue, and identify areas for improvement. Measure conversion rates at each stage and prioritize promising prospects to optimize sales conversion rates.
7. What are some common sales methodologies?
Sales methodologies help teams engage prospects, understand their needs, and close deals. These methods help boost sales and conversions. Here are some common sales methodologies:
SPIN Selling:
SPIN stands for Situation, Problem, Implication, and Need-payoff. By asking questions, salespeople can better understand a prospect’s situation, problems, and implications.
MEDDIC:
MEDDIC is an acronym for Metrics, Economic Buyer, Decision Criteria, Decision Process, Identify Pain, and Champion. This method qualifies leads and identifies pain points.
Miller Heiman Strategic Selling:
This methodology emphasizes identifying key decision-makers, understanding their needs, and building strong relationships throughout the sales process. It tracks opportunities formally.
BANT (Budget, Authority, Need, Timeline):
BANT evaluates a prospect’s budget, decision-making authority, product or service need, and decision timeline. It helps prioritize leads.
GAP Selling:
GAP Selling identifies a prospect’s “gap” between the current and desired state. Salespeople identify this gap and present their product as the solution.
N.E.A.T. Selling:
Navigate, Engage, Activate, and Transform—N.E.A.T. This method helps prospects navigate their buying journey through these four stages to close deals quickly.
SNAP Selling:
Simple, iNvaluable, Aligned, and Priority—SNAP. This approach simplifies prospects’ decision-making, shows value, aligns with their goals, and prioritizes the offering.
Social Selling:
This modern approach leverages social media platforms and online networks to build relationships and engage with prospects more personalized and relevantly.8. How does consultative selling differ from traditional sales approaches?
Traditional and consultative sales differ in focus, customer interaction, and methodology.
Consultative selling prioritizes customer needs. Salespeople listen to identify individual problems. They then tailor solutions to these needs, fostering customer-centricity and long-term relationships.
Traditional sales focus on the product. Instead of exploring the customer’s unique situation, focus on features and benefits. Sales goals may overshadow relationship-building. Consultative selling involves problem-solving. Salespeople identify customer needs and sell the product. This method promotes open-ended questions and dialogue to better understand customer needs.
In traditional sales, the salesperson does most of the talking and persuasion. Product features and pricing may be prioritized over customer issues. Consultative selling prioritizes value-added interactions. It provides insights, expertise, and customized solutions to customer challenges or goals, resulting in a mutually beneficial outcome. Traditional sales can be product-focused with standardized pitches and transactions.9 What do we mean by sales?
When we refer to “sales,” we are talking about the process of transferring goods or services from a seller to a buyer in exchange for money or other forms of compensation.
Sales encompasses a range of activities including identifying potential customers, engaging them through various channels, understanding their needs, and ultimately concluding a transaction where the buyer pays the agreed-upon price.
The term, “sales” can also refer to:
– The total amount of goods or services sold during a specific time period.
– The revenue generated from selling goods or services.
– A department or team within a company responsible for selling its products or services.
Sales is a critical function in most businesses as it directly impacts revenue generation and growth.10 What is sales in a business?
In business, “sales” refers to the process of selling a product or service to customers, resulting in revenue for the company.
Sales encompasses various activities that lead to the transfer of ownership or agreed-upon provision of services in exchange for money or other forms of compensation.
Sales is a vital function in most businesses, driving revenue, growth, and sustainability.11 What is sale in marketing?
A “sale” in marketing is the successful transaction or conversion in which a consumer chooses to buy a good or service, transitioning from a possible or interested buyer to an actual customer.
A more thorough explanation of the phrase in the context of marketing is provided below:
– End of the Marketing Funnel: The conclusion or end of the marketing funnel is often thought of as a sale. Through a variety of marketing techniques, the objective is to encourage the consumer to make a buy, which is the sale, after increasing awareness, piqueing interest, and creating desire.
– How many sales were produced is the determining factor in the success of many marketing strategies. Sales are frequently the most obvious return on investment (ROI) for marketing initiatives, despite the importance of other measures (such as engagement, brand awareness, or lead generation).
– Consumer Conversion: The sale is the moment a potential client turns into a paying client. Advertising, content marketing, social media promotion, email marketing, and other marketing techniques can all contribute to this conversion.
– Building Relationships: Although the sale is an important turning point, contemporary marketing does not see it as the end of the relationship. Instead, it serves as a starting point for post-sale marketing initiatives like loyalty schemes, customer retention plans, and up- or cross-selling chances.
– Feedback Loop: Sales information, such as volume, frequency, and buyer demographics, offers marketers useful feedback. Future product offerings, marketing strategies, and client interaction techniques can all benefit from the knowledge provided.
While the “sale” is an important marketing indicator, the focus is also placed on the entire process leading up to that sale as well as the possibilities that present themselves after the sale to nurture and develop the customer relationship.12 Why is it called “Sales”?
The word “sales” originally came from the Old English word “sellan,” which meant “to give, furnish, supply, or deliver.” The meaning evolved to refer to exchanging goods or services for money. The process of persuading a potential client to make a purchase is what this term refers to, and it is crucial to the success of any company.
13 What is the Sales Formula?
The sales formula may change depending on the situation and the aspect of sales being analyzed. Nonetheless, here is a standard procedure for estimating sales proceeds:
Sales Revenue = Number of Units Sold × Price per Unit
Knowing how much a company earns from sales is crucial for budgeting, planning, and assessing the efficacy of sales strategies.14 What is Sales and Example?
The term “sales” describes the actions that lead to exchanging goods or services between a buyer and a seller in exchange for money. A good illustration of sales activity is selling a novel by a bookstore to an individual customer. The bookstore makes money from selling the book to the customer.
15 What is the Sales Process?
To convert a prospect into a paying customer, businesses employ a series of steps known as the sales process. A sales process usually consists of the following stages:
1 Prospecting is the process of locating possible clients
2 Connecting: Making a connection and establishing communication.
3 Qualifying: Assessing the potential customer’s needs and ability to purchase.
4 Presenting: Demonstrating the value of the product or service.
5 Handling Objections: Addressing any concerns or hesitations.
6 Closing: Completing the transaction and guaranteeing client satisfaction.
7 Follow-up: Preserve the connection in case future business or recommendations arise.16 What is the Role of Sales?
Salespeople’s job is to connect the company’s goods and services and the clients who require or desire them. Salespeople have the following responsibilities:
1 Developing Relationships: Forming and upholding connections with clients.
2 Understanding Customer Needs: Identifying what customers want or need.
3 Communicating Value: Demonstrating how the product or service meets the customer’s needs.
4 Closing Deals: Finalizing sales transactions.
5 Meeting Sales Targets: Reaching the company’s predetermined sales targets.
6 Offering Post-Sale Support: Guaranteeing client contentment and resolving any issues that arise after the sale.How do B2B Sales Work?
Business-to-business, or B2B, sales are those that take place between companies. B2B sales are when a company sells goods or services to another company. Frequently, the procedure entails –
– Longer Sales Cycles: Because of the complexity of the transactions and the number of stakeholders involved, B2B sales usually take longer to close.
– Higher Transaction Values: B2B transactions often involve larger quantities or more expensive products/services.
– Relationship Building: In B2B sales, a solid rapport and foundation of trust is essential.
Negotiation: Regarding terms, conditions, and price, there is usually more room for discussion.
14. What are the Four Types of Sales?There are various ways to categorize sales, but one common classification includes
– Inside Sales: Sales are conducted remotely, often via phone or email.
– Outside Sales: Sales are conducted in person, often through meetings or site visits.
– B2B Sales: Business-to-business sales, where one business sells to another.
– B2C Sales: Business-to-consumer sales, where a company sells directly to individual consumers.







