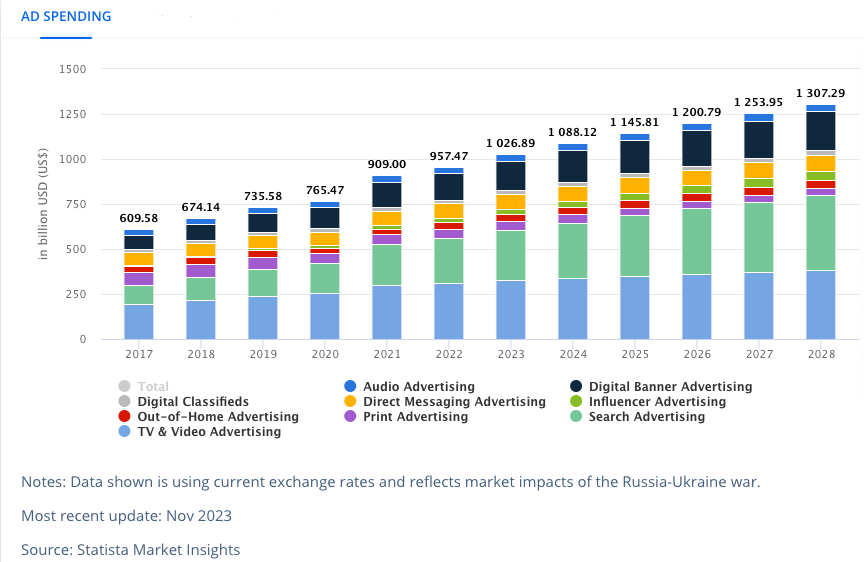
By 2028, global advertising spending will be approx US$1307 billion. But what is advertising, and why do businesses devote so much money to it? Simply put, advertising is paid promotional messaging distributed through various media (such as TV, radio, print, digital, outdoor, etc.) to inform, persuade, or remind audiences about specific products, services, ideas, or causes.
Advertising may take many shapes, from eye-catching billboards to inspirational social media postings to 30-second movie theater commercials, but they all serve the same underlying purposes.
Advertisers construct messages meant to appeal to target customers on emotional and rational levels, whether selling automobiles, shoes, cosmetics, or humanitarian causes. The ultimate goal is to boost brand recognition, educate on product advantages, drive sales or contributions, or link pleasant images with a name.
While some people see advertising with skepticism or misunderstanding, those in charge of multibillion-dollar campaigns see it as serious business essential to attaining economic success and development in competitive marketplaces.
Effective advertising necessitates creative content and intelligent media placement, but it also depends on knowing consumer insights and psychology to impact actions. Advertising has become firmly ingrained in popular culture, fueling the economic fortunes of businesses, media networks, and others. As one of the top Advertising agencies in India, we at BrandLoom can help you build the best advertising strategy to reach your target audience and resonate with them.
What is Advertising?
Advertising is a critical component of marketing communication, carefully designed to display products, services, and ideas to varied audiences across various media channels. The primary goal is to capture attention, develop interest, increase awareness, give detailed information, convincingly express value, and urge a specific action, such as a purchase, contribution, or desired response.
The spectrum of advertising mediums includes conventional channels such as television, radio, print publications, and billboards, as well as the dynamic landscape of digital platforms such as social media and other developing digital spaces.
Specialized enterprises in the advertising sector focus on market research, creative ad development, media planning and purchase, production, analytics, and more. Ad agencies, in-house marketing teams, media firms selling ad space, tech suppliers, and independent artists and influencers are critical participants.
Advertising has limitless creative potential, frequently employing attention-grabbing images, relatable characters, narrative, comedy, celebrities, catchy jingles, emotional appeals, inclusive representation, and other inventive strategies to engage consumers.
Advertising tactics, messages, brand image, and calls to action are all based on market research on target demographics and customer behavior. Effective advertising reflects public mood and changes attitudes and popular culture.
The advertising sector constantly faces upheaval in the ever-changing world of digital media consumption and must adapt creatively to attract consumer engagement. The astonishing success of social media advertising illustrates this space’s flexibility and promise. Finally, advertising generates trillions of dollars in economic activity and helps fund the development of free, ad-supported content consumers appreciate.
Definition of Advertising
Advertising is advertising a product, carrier, or idea to a target market to influence their attitudes and actions. It involves developing and distributing convincing messages over numerous media structures, including TV, radio, print, internet, and social media.
Advertising’s key objectives are to construct consciousness, enlighten potential customers, establish a fantastic logo photograph, and ultimately force sales or preferred behaviors.
Advertising might also take a whole lot of paperwork, which includes:
- Promotional communications: This type of content wants to educate and persuade clients about a product, provider, or emblem. They often emphasize features, blessings, and specific selling factors.
- Branding: Advertising is critical in developing and maintaining a logo’s identity, persona, and photograph in clients’ eyes. It helps to construct emblem focus, loyalty, and difference.
- Public service announcements (PSAs): They are classified ads that promote social causes, public fitness initiatives, or significant public concerns rather than industrial items or offerings.
- Sponsorships and endorsements: Companies frequently guide activities, groups, or human beings in return for promotional blessings and emblem reputation.
Effective advertising and marketing campaigns often encompass marketplace research, innovative introduction, media approach, and performance evaluation. Advertisers utilize several strategies to attract clients’ attention and affect their behavior, including emotional appeals, comedy, celebrity endorsements, and unusual pix.
Advertising is a multibillion-dollar enterprise that shapes patron choices, fuels monetary development, and affects society’s tendencies and values.
Characteristics of Advertising
Advertising has specific features that distinguish it as a compelling and creative commercial force. This section digs into the fundamental characteristics of the dynamic advertising environment, from its multi-media reach to its effect on popular culture:
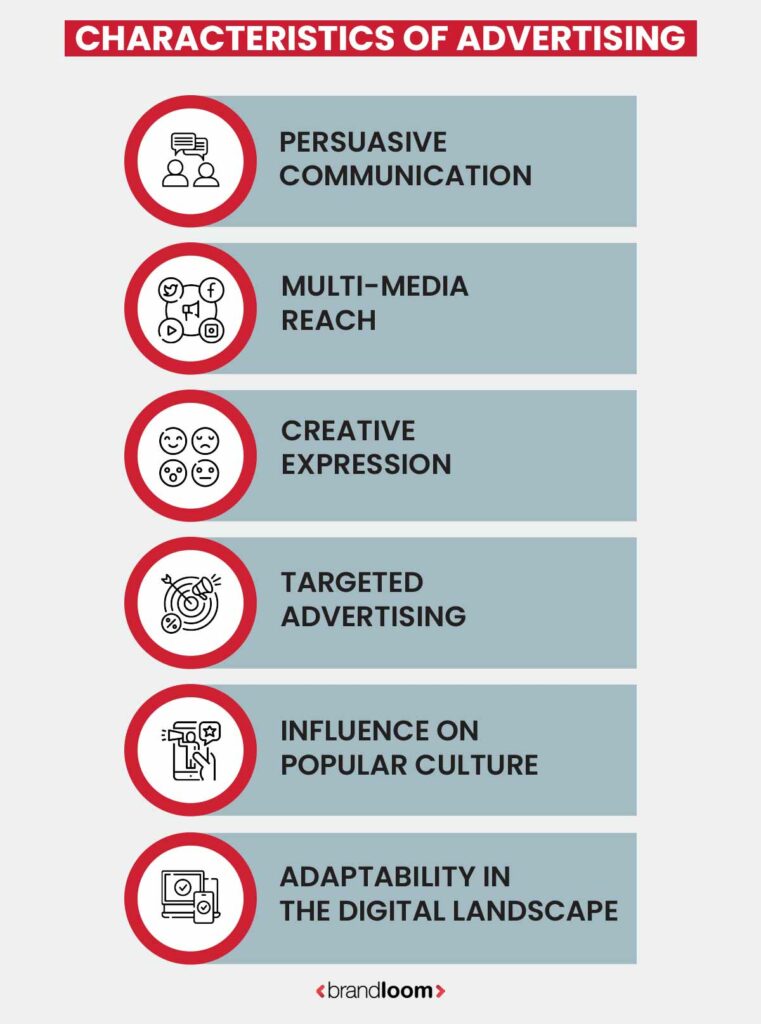
1. Persuasive Communication:
Advertising persuasively influences customer behavior and attitudes about a product, service, or concept. Advertising attempts to persuade people to do a specific action or hold a particular opinion by using captivating language and imaginative imagery.
2. Multi-Media Reach:
Advertising utilizes various media channels, including television, radio, print publications, billboards, social media platforms, and numerous digital formats. This multi-media strategy guarantees that advertising messages reach a diverse audience.
3. Creative Expression:
Advertising depends on innovation, employing attention-grabbing graphics, narrative, comedy, emotional appeals, and other novel strategies to capture and engage people. Advertising creativity is critical for leaving a lasting impression and developing brand identification.
4. Targeted Advertising:
Effective advertising caters to specific demographics and customer habits. Advertisers design ideas and graphics that appeal to the intended demographic through rigorous market research, boosting the effectiveness of their campaigns.
5. Influence on Popular Culture:
Advertising reflects public feelings and has a huge impact on attitudes and popular culture. Memorable advertising campaigns can shape cultural norms, attitudes, and customer preferences.
6. Adaptability in Digital Landscape:
As the digital environment evolves, advertising must constantly adapt to new platforms and technologies. The adaptability of digital advertising enables real-time modifications and individualized targeting, assuring relevance in a media landscape that is becoming increasingly fragmented.
Importance of Advertising
Advertising’s relevance stretches beyond conventional promotion, covering economic, social, and cultural significance. Its power to influence cultural discourse, affect customer behavior, and drive economic growth highlights its critical position in modern business. Let’s take a look at some of the importance of advertising:

1. Brand Visibility and Recognition:
Advertising has a significant impact on brand visibility and recognition. Advertising guarantees that companies remain top-of-mind for customers through clever placement and appealing messages, establishing familiarity and trust.
2. Revenue generating:
By boosting sales and expanding market share, effective advertising immediately helps increase revenue. Well-crafted ad campaigns can attract new consumers, retain existing ones, and ultimately increase a company’s bottom line.
3. Consumer Education:
Advertising is a forum for teaching customers about product features, advantages, and unique selling propositions. Informative ad content enables consumers to make more educated purchase decisions, ultimately improving their brand experience.
4. Market Competition:
Advertising is critical in differentiating a brand from its competitors in a competitive marketplace. Advertising allows firms to build a distinct identity and stand out among competitors by emphasizing distinctive selling factors and value propositions.
5. Economic Impact:
Advertising stimulates economic activity by assisting businesses, creating jobs in the advertising sector, and contributing to general economic growth. It creates demand, boosts consumer spending, and promotes innovation and entrepreneurship.
6. Influence on Society and Culture:
Advertisements frequently reflect and affect society’s values, trends, and cultural standards. They can start conversations, raise awareness about social concerns, and influence constructive social change.
7. Innovation and Creativity:
The advertising business lives on innovation and creativity, continually pushing the envelope to generate compelling and memorable campaigns. This emphasis on creativity motivates artistic expression and develops an innovative culture within the sector.
Objectives of Advertising
Advertising plays several vital functions that help organizations reach their advertising and communication targets. The number one purpose of advertising and marketing may be normally classified as follows:
Increasing Brand Awareness:
One of the key dreams of marketing is to broaden and raise brand recognition among prospective purchasers. Advertising aids in introducing a brand, its items, or its offerings to the intended target audience and organizing a presence inside the marketplace.
Informing and Educating:
Advertising seeks to enlighten customers approximately a product’s characteristics, blessings, and particular selling points. It advises clients about the supply of a product or service, its programs, and how it can meet their necessities and dreams.
Creating Positive Brand Affiliations:
Advertising impacts customers’ perceptions and affiliations with a logo. Advertising uses innovative messages and imagery to construct top emblem connections, increase a unique personality, and separate the employer from opponents.
Persuasion and its effect on:
Advertising uses persuasive techniques to affect customer attitudes, ideals, and moves. Its purpose is influencing the target audience to take a particular movement, including shopping for a product, trying out a career, or assisting a purpose.
Reinforcing Brand Loyalty:
Advertising is essential in maintaining emblem loyalty amongst cutting-edge consumers. Advertising strengthens the brand-purchaser connection by continuously conveying brand messaging and reminding consumers of the business enterprise’s value proposition.
Increasing Sales:
Advertising aims to boost an organization’s sales and earnings. Advertising stimulates the call for and encourages buying alternatives by way of growing logo recognition, developing favorable emblem impressions, and convincing customers.
Supporting Other Marketing Efforts:
Advertising complements different marketing operations with public relations, direct advertising, and sales promotions. It dietary supplements and strengthens these efforts to develop a unified and hit advertising plan.
Advantages of Advertising
Advertising affords widespread benefits to each organization and its customers. Some of the primary benefits of advertising encompass:
- Increasing logo cognizance and reputation – Advertising exposes customers to brands, goods, and services, increasing the probability that they will consider the emblem after they need that product or service. Effective advertising campaigns can also significantly grow emblem recognition and assist agencies in constructing an emblem identification.
- Educating clients – Advertisements may inform clients about new items or functions and educate them on the benefits and packages of an agency’s services or products. This allows customers to make more excellent, educated purchase choices.
- Increased sales – Businesses sell to sell extra objects or offerings. Well-focused commercials that reach the perfect customers at the right time can also grow sales or leads for businesses. This will increase the consumer base and provide more money.
- Supporting mass manufacturing – Advertising introduces and promotes new heavily produced gadgets to a big target audience. This increases demand, permitting companies to gain from economies of scale and reduced manufacturing fees in line with units.
- Providing jobs – The advertising sector employs entrepreneurs, designers, researchers, salesmen, and other professionals throughout organizations and media resources. It increases economic hobby.
- Lowering consumer costs – Media retailers fund content material and users get the right of entry through the sale of the marketing area. Consumers eventually pay much less for ad-supported content than material sponsored entirely via subscriptions or prices.
Disadvantages of Advertising
While advertising provides blessings, a few downsides and critiques of advertising and marketing include:
- Increased prices for corporations—Advertising can be high-priced, specifically on large media platforms. Companies need to examine expanded promotional expenses against possible sales advantages. Small companies with tight resources might struggle to have enough money for effective marketing.
- Contributes to increased purchaser fees – Better retail pricing allows customers to surpass advertising costs directly. This results in inflation, making gadgets more expensive.
- Can be misleading – Companies may also exaggerate or omit records in advertisements to make things seem greater suited. This would possibly mislead customers and bring about sadness with their goods. Strict legal guidelines exist to prevent fraudulent marketing.
- Encourages immoderate consumption – Advertising increases demand by way of attracting human beings to purchase matters they may now not surely want. This promotes wasteful intake and excessive materialism, which harms the surroundings.
- Creates desires and dissatisfaction – Advertising creates demands and unhappiness by constantly displaying idealized snapshots and life, which in reality can’t be healthy. This may lead to sadness, which has a bad effect on mental fitness and shallowness.
- Interrupts content material studies – Ad placement may also interrupt and interfere with consumer stories, such as watching TV or surfing the internet. Consumers find disruptive advertisements bothersome.
- Invades privateness – Highly focused virtual classified ads rely upon gathering personal records and online surfing records, causing growing privacy problems regarding how purchaser records are amassed and applied.
Types of Advertising
1. Print Advertising
Print advertising encompasses conventional offline channels such as newspapers, periodicals, flyers, brochures, and direct mail. Marketers may use visual components such as high-resolution photographs and graphics to attract readers’ attention when developing advertising for print media. Print advertising has a permanence that digital ads do not have since readers may preserve print ads and refer to them later.
Print advertising, on the other hand, is losing appeal and efficacy as more people consume news and information online. Younger generations, in particular, eschew traditional print media. However, some publications and demographics continue to engage with print daily.
Thus, targeting older age groups and those interested in certain hobbies or sectors covered by magazines and newspapers is still important. The style and placement of a print advertisement may significantly impact the degree of exposure and memory it receives from readers.
2. Broadcasting Advertising
Commercials broadcast on radio and television are examples of broadcast advertising. Ads are aired on the radio between songs or programs to target consumers during everyday commutes or activities. Television advertising provides for targeted programs or time slot targeting, yet consumers are increasingly skipping or ignoring advertisements.
Product placement interwoven tastefully into TV program plotlines is another option. Radio and television reach large audiences but have fewer targeting choices than Internet advertising. Tracking returns is likewise tricky; therefore, broadcasting is best utilized with more quantitative methods.
3. Online Advertising
Online advertising includes display, search, social media, and video ads. Digital advertising has the advantage of being highly targeted based on people’s online profiles, demographics, hobbies, and prior online behaviors gleaned from search history and social media activity.
Marketers may direct their advertising to potential customers interested in a product or service. Clicks, conversions, and other statistics are also easily trackable in online advertising, allowing marketers to optimize expenditures and find the most efficient approaches. As a result, online advertising has expanded quickly in the last several decades.
4. Mobile Advertising
Mobile advertising is commercial content that appears on cell phones and tablets. Marketers are increasingly adopting in-app, banner, and other formats intended for small displays as mobile device adoption expands fast. Mobile allows for geo-targeting adverts based on a user’s specific location, enabling location-based targeting.
Proximity marketing may contact customers on their mobile devices while they are close to a business. Because individuals spend so much time on their phones, engagement with mobile advertisements is strong. Ads linked to mobile applications may also track app installations and other information for analyzing ad performance.
5. Product Placement
Product placement is the deliberate incorporation of brand names, products, or services into television shows, films, novels, and other forms of media output. Instead of typical commercials, product placement tries to quietly introduce target people to a brand while they are absorbed in entertainment.
This form of integrated advertising is becoming increasingly popular for businesses to get their products seen without interfering with programming flow. While subtle, product placement may raise awareness if done smoothly as part of the media plot. It is challenging to quantify efficacy, but it offers exposure to large audiences.
6. Direct Mail
Direct mail advertising entails providing tailored communications to consumers by postal mail, such as catalogs, postcards, letters, and parcels. Marketers use consumer data to deliver direct mail to lists of people most likely interested. While mail volume has decreased, direct mail continues to reach consumers at home, where they are more attentive than advertising.
It enables the integration of multimedia components such as images in print form. Tracking response rates via coupons or reply cards aids in determining the performance of direct mail compared to other channels. The disadvantages include more significant expenditures and the possibility that communications may not be opened.
7. Out-of-home Advertising
Out-of-home advertising displays big format advertisements in public areas where people walk daily. This includes billboards, bus shelters, telephone kiosks, and other buildings in public places such as streets and shopping malls. It exposes captive consumers who may see an ad during commuting or errand times as an ambient advertising approach.
Marketers may geo-target OOH advertisements to specific communities or commuting routes. While reaching many people, monitoring efficacy is difficult since consumers may not recall brand exposures via public signs. Location-based targeting and analytics are now possible with new digital formats.
Challenges of Advertising
While advertising has numerous advantages for organizations, it also has some fundamental issues that marketers must overcome. Here are a few challenges that you should keep an eye out for:

1. Avoiding Ad Fatigue
Breaking through the advertising clutter to engage target consumers is one of the main challenges marketers face. Consumers are inundated daily with hundreds of marketing messages across multiple media, prompting many to experience “ad fatigue.” It has grown more challenging to make advertisements stand out and capture someone’s attention in the middle of the racket.
2. Determining ROI of Advertising
Another problem is determining the natural effect and ROI of advertising investment. While digital channels enable sophisticated data, attributing physical purchases to individual advertising remains an imprecise science. It is difficult to distinguish the impact of advertising from other brand-building variables. Marketers frequently struggle to determine which strategies are the most cost-effective.
3. Keeping Content Fresh
Keeping advertising campaigns fresh and exciting throughout time is a continual challenge. Constant pressure exists to outperform prior attempts to avoid listeners tuning out repeating messaging. Changing tactics too often, on the other hand, risks confusing customers and causing a lack of consistency. Marketers face difficulty in finding the correct mix of development and consistency.
5. Regulations and Law
Ad content and claims must adhere to various industry and regulatory rules. Oversights may result in penalties or legal action. Furthermore, consumer privacy concerns have resulted in stricter data limits, eroding particular targeting possibilities. Compliance with legislation such as GDPR increases administrative costs.
6. Budget Restriction
Budget restrictions are an ongoing concern. Significant corporations must carefully distribute limited marketing funds across several channels and goals. Measuring ROI is critical for demonstrating the benefit of advertising to executives to get continuous financing. However, certain significant public awareness efforts may not provide quick returns on investment.
7. Staying Updated with the Latest Technology
Keeping up with rapid technological advancements is another difficulty for marketers. Influencer marketing, for example, necessitates the development of new talents and evaluation methodologies. Resources must constantly modify messages and methods to remain relevant in altering online and offline customer habits. If you do not develop, you risk becoming outdated.
Overcoming these challenges necessitates continuous testing, creativity, and adaptation to the changing advertising scene. However, marketers who can negotiate these hurdles most successfully will be best positioned to create long-term benefits for their businesses.
Steps Involved in Advertising

1. Planning
The planning step is essential to the success of a campaign. Marketers must first define SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound) objectives. These goals serve as the foundation for all future actions and give explicit measures for evaluation.
Thorough primary and secondary research is undertaken to obtain consumer insights into the target audience’s demographics, psychographics, habits, pain areas, and motives. Competitive intelligence examines what rivals are doing well as well as market opportunities.
Based on research findings, creative briefs highlight the core messaging and value propositions to express. These briefs serve as guidelines for the creative team. Media planners study the target audience’s usual media consumption patterns simultaneously to discover the best channels for reaching them. Print, digital, television, radio, and other mediums are evaluated along with financial allocations.
2. Creation
Ideas emerge after much investigation and forethought. Creative companies collaborate closely with clients to develop concepts, slogans, visual designs, and overall messages that are specific to the target market. Early models go through consumer idea testing to determine message delivery and likeability. Valuable input aids in the refinement of the creative direction.
3. Implementation
The optimized campaign is now ready for deployment. Media space and time are secured through long-term contracts. Production of finalized creative assets such as commercials, banners, print advertisements, and material begins. Campaigns are methodically planned for distribution across all specified channels per placement guidelines.
4. Tracking and optimizing performance
Analytics dashboards give real-time insights into website and shop traffic, app usage, conversions, and more throughout the campaign. How objectives are met is regularly checked for underperforming parts. Testing different messaging, channels, placements, or remarketing might assist in increasing engagement. To increase results, insights drive optimization decisions.
5. Continuous Evaluation and Improvement
Following completion, marketers do extensive reviews. Data is evaluated to assess whether or not objectives were met and to compute ROI. Reports describe the lessons learnt from performance indicators and stakeholder input. Valuable learnings are subsequently fed into the next iterative planning cycle, where knowledge is applied to enhance future campaigns through continual testing and refining.
Good Examples of Advertising
1. Apple iPod silhouettes Ad Campaign
Apple launched a revolutionary advertising campaign for the iPod in 2003, which helped propel the company to new heights.
The stark white Apple logo, iPod trademark, and gadget stood out in contrast to the luscious colors. This basic yet visually stunning design began to appear on billboards and newspaper advertisements throughout major cities.
While the items were not presented directly, the advertisements skillfully emphasized the iPod’s function in enabling customers’ own expression through music. They recorded people’s excitement and freedom while listening on the go.
On television, the ad was brought to life by silhouettes dancing to famous tunes of the period. Despite being a break from more traditional product-focused advertisements, the ads had a tremendous impact on audiences.
Steve Jobs initially doubted that not openly promoting the iPod would be helpful. The campaign, on the other hand, was a huge success, earning multiple creative honors.
It fueled significant development for the iPod and Apple by capitalizing on the emotions associated with music. Advertising became synonymous with the business and its ability to incorporate music into people’s lives effortlessly.
This creative approach illustrated how advertising does not necessarily need to focus on features but can be equally effective when expressing a product’s impact and advantages through a vibrant and visually attractive narrative. It reinforced Apple’s creative image and ushered in a new era of basic yet effective commercial design.
2. Spotify Embarrassing Listening Habits
Spotify introduced an unusual out-of-home advertising campaign in 2016 that highlighted its members’ different listening patterns. The commercials, designed by Spotify’s in-house creative team, took over high-traffic billboards in key cities.
Each billboard exhibited amusing yet relevant listening behaviors in a meme-like manner. The advertisements caught several classic music-listening scenarios, from bingeing sad tunes amid a breakup to crafting the ultimate exercise playlist.
Despite Spotify being a renowned digital music company, this campaign was unique because it used classic offline advertising channels such as billboards. This exemplified the company’s insight that multiple channels frequently connect individually with different audience segments.
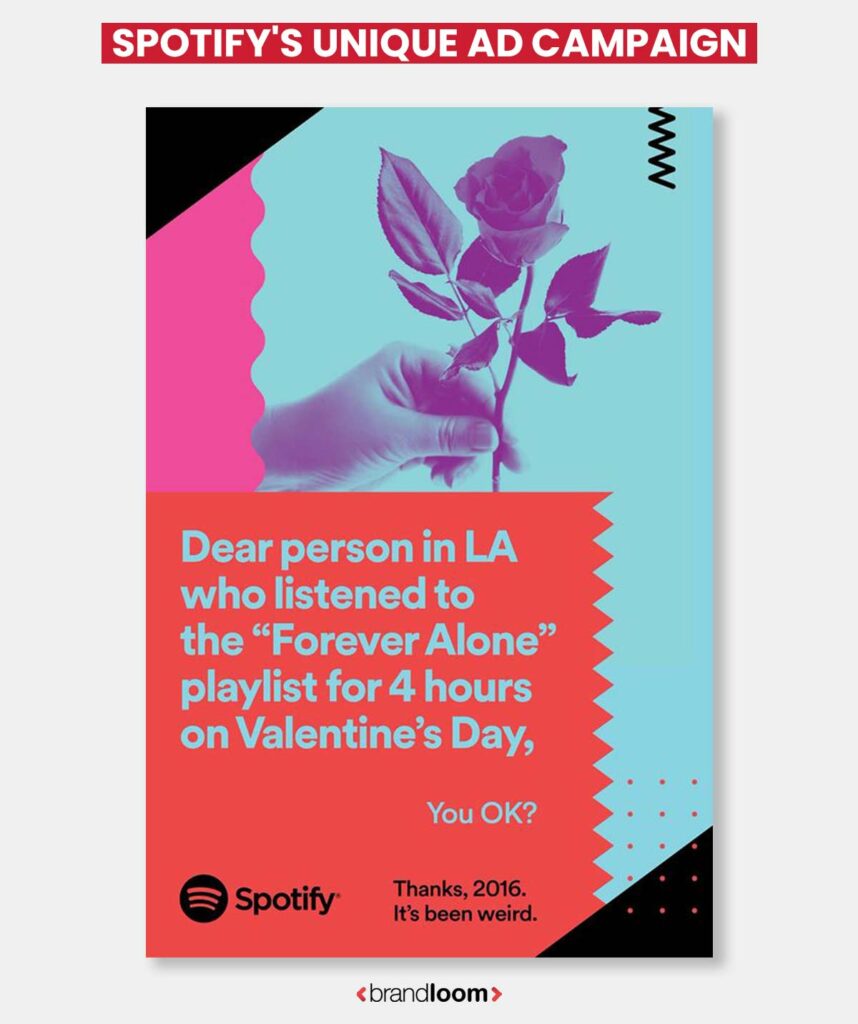
Spotify was able to cut through the digital clutter and engage with listeners in a fun, engaging manner by bringing its brand message straight to where consumers spend their daily commutes and routines. The realistic advertisements emphasized Spotify’s importance in its vast user base’s daily lives and emotions.
This innovative, multi-pronged strategy demonstrated how even the most prominent internet firms may profit from print and outdoor advertising placements to reach a broader audience. It demonstrated that the dominance of digital media does not prevent experimenting with complementing conventional media to increase awareness and engagement. The amusing memes contributed to Spotify’s status as more than simply music software; it was also a cultural phenomenon.
3. Nike’s Famous “Just Do It” Ad Campaign
Nike initially targeted marathon runners and other endurance athletes with their merchandise. However, a new fitness fad was sweeping the country in the 1980s. People were becoming more active and exercising regularly.

Nike’s marketing staff recognized this as an opportunity. Reebok, their major competition, was now outselling them. So they set out to build a campaign that would capture the spirit of this new fitness movement and pique the interest of more casual exercisers in the Nike brand.
They debuted the now-iconic “Just Do It” tagline in 1988. It was an instant hit. The two simple sentences wonderfully summarized people’s desire and passion when working out. “Just Do It” appealed to our inner voice, encouraging us to push ourselves, whether running 5 miles or going up the stairs.
The outcomes spoke for themselves. Nike’s yearly revenues were $800 million in 1988. They had risen to almost $9.2 billion in just ten years. “Just Do It” became one of advertising’s most famous taglines.
The most important takeaway from Nike’s experience is the value of really understanding your target audience. Nike crafted a message that resonated deeply by understanding the primary motivations and challenges exercise solved for most people.
Why Should You Hire an Agency For Advertising?
Hiring an agency to manage their advertising is a wise decision for many firms. Advertising is a complicated industry that needs analytics, creative design, media purchasing, and campaign optimization knowledge. It’s tough for one individual to be an expert at everything unless you have a substantial in-house marketing team with specialists in all these positions.
An intelligent digital firm would have implemented effective advertising strategies across several channels for diverse customers. They are aware of what works well in each business and demography. Their unique understanding may assist you in maximizing the return on your advertising investment.
Agencies also remain up to date on the newest digital trends and changes. They understand how customer behavior shifts across platforms like search, social media, and programmatic display advertisements. They may propose tweaks that keep your campaigns functioning at their best by continually reviewing performance data.
Hiring an agency such as BrandLoom allows you to take advantage of economies of scale. They have established ties with platforms and can negotiate better pricing on media purchases than a single company. Another cost-effective advantage over employing numerous in-house jobs is their vast experience.
For a company focused on its core activities, an agency may handle everything from strategy to execution to reporting. This frees up your time and resources to focus on other growth areas. An agency is also an excellent alternative when your company grows, and your demands become more complicated.
In conclusion, collaborating with a digital marketing firm is a wise outsourcing move that may dramatically improve the outcomes of your advertising campaigns. Pick an agency with a track record of success in your business vertical and align your goals throughout onboarding.
Conclusion
To summarize, advertising is critical in today’s business environment since it helps to market companies, goods, and services. Effective advertising delivers the correct message to the target audience through the strategic use of numerous media channels, whether the aim is to promote awareness, consideration, or purchase.
It enables businesses to enlighten potential clients about what they provide and why their solutions are preferable to rivals’. While technical developments have caused advertising to vary dramatically, its essential functions have remained consistent: to grab attention, hold interest, build desire, and eventually compel action.
Businesses that invest in excellent, targeted advertising, whether through old mass media or newer digital channels, stand to gain a competitive advantage by expanding their client base and increasing revenues. Advertising may be a highly successful marketing strategy for any organization with proper preparation and assessment of outcomes. If you require a strong advertising campaign to boost your sales and reach, you can contact us at BrandLoom, as we are one of the leading advertising agencies in India.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the different types of advertising?
Print advertisements, such as those that appear in newspapers and magazines, are among the various forms of advertising. On channels and websites, there are also video and television advertisements. Another popular format that incorporates advertising on discussion and music channels is radio.
Online advertising includes sponsored search advertisements on search engines such as Google and display ads on websites and applications. Social networking sites provide advertising opportunities as well.
Outside-the-home advertising is typical, with billboards and posters erected in busy locations. New media forms include product placement in TV series, films, and videos; influencer marketing through social media influencers; and podcast sponsorship.2. What are the main goals of advertising?
Broadly speaking, the primary objectives of advertising are to increase awareness, alter public opinion, and generate leads or sales. Developing top-of-mind recognition for the brand, good, or service is known as building awareness.
Changing perception involves enhancing or molding one’s reputation and public image. While creating immediate transactions drives sales, gathering contact information for potential future sales possibilities is the goal of building leads.
Loyalty programs and advocacy aim to convert content consumers into devoted brand ambassadors over time. Together, these objectives boost revenue and wrest market share from rivals.3. How do I measure the effectiveness of an advertising campaign?
Businesses frequently monitor essential indicators associated with their marketing goals to assess effectiveness. Surveys can measure both assisted and unassisted recall if brand awareness is the desired outcome.
Campaigns for sales need to track income, conversion rates, and units sold. To calculate return on investment, monitoring expenses and contrasting them with outcomes (ROI) is critical.
Platform analytics solutions offer information on clicks, impressions, engagement, and transactions, allowing analysts to assess which placements and ads elicited the most reactions from viewers. It provides insights to test various creatives, formats, and targets.4. What makes a good advertising message?
A solid call to action is essential to every successful advertising campaign. This instructs the viewer on the precise action to perform, including clicking to find out more, contacting a number, or going to a website.
It should also emphasize the salient features or USP that set the good or service apart from rival offerings. Using language and visually attractive imagery that appeals to the target audience also makes a difference.
Using relevant targeting, the advertisement is guaranteed to be seen by people most likely to act on it. The likelihood of a favorable reaction rises as a result.5. How much should a business spend on advertising?
There is no standard budget % since it varies widely depending on the sector, degree of competition, campaign objectives, and resources available. Nonetheless, many professionals advise devoting 2–10% of yearly income to marketing and advertising initiatives.
Younger startup businesses could have to make more significant investments until their brand becomes well-known. Even with lower spending, well-known companies must experiment with new tactics and distribution methods.
By routinely evaluating the outcomes, one may allocate funding as efficiently as possible among the most affordable strategies to achieve the targeted goals, such as leads, sales, or business-specific brand KPIs. To optimize results, testing is crucial.What is Surrogate Advertising?
Surrogate advertising, also called oblique advertising or camouflage advertising and marketing, is a type of advertising tactic that promotes prohibited or limited gadgets, including alcohol, cigarettes, or different regulated drugs, by advertising and marketing associated or unrelated items or offerings.
In many nations, advertising for specific items, including tobacco or alcoholic beverages, is outlawed or subject to stringent controls. Surrogate marketing permits businesses to get around these limits via advertising and marketing a separate product or service that isn’t always issued to the same marketing rules.
Surrogate advertising and marketing aim to increase logo know-how and not forget about the prohibited product, even supposing the campaign does not explicitly sell it. Companies make use of quite a few techniques to try this, which include:
Brand Extension: Companies increase a brand extension for a separate, unrelated service or product with a comparable call, logo, or photographs to the restrained product. This enables the maintenance of brand familiarity and linkages with the unique product.
Product Diversion: Businesses marketplace a similar or complementary product or service that isn’t always explicitly prohibited but has connotations with the forbidden product. For example, a tobacco firm may additionally marketplace smoking accessories, lifestyle apparel, or logo-related activities.
Pics and Symbolism: Advertisements may additionally consist of subtle images, symbols, or shades that can be firmly diagnosed with the precise product or its target demographic. This helps to construct oblique logo connections without overtly naming the product.
Lifestyle selling: Instead of promoting the product, corporations market a lifestyle or attitude or revel in this, which is carefully related to the restrained product. This strategy establishes an emotional reference to the target audience and develops brand loyalty.What is the Difference between Advertising and Personal Selling?
Like the two sides of the marketing coin, personal selling and advertising are trying to entice you to buy, but in very different ways.
Advertising’s purpose is to cast a wide net. It reaches a broader audience through attractive images and messages on television, radio, billboards, and social media. A vendor will roar from a rooftop at anyone who comes along. Advertising is highly effective in generating leads, stimulating interest, and establishing brand recognition.
The approach to personal sales is more intimate. The agent communicates directly with the potential customer one-on-one. They can tailor their presentations to the client’s specific requirements and answer questions in real time. Compared to the talk, the salesperson guides the customer towards a purchase while establishing a relationship. Where consumers need the extra push, hard products or expensive products are the key products they can sell to themselves.What do you mean by advertising?
Advertising is a form of marketing communication that promotes or sells products, services, or ideas to a target audience. It involves the paid, impersonal, and public dissemination of information and promotional messages across multiple media channels.
Some of the most essential elements of advertising are:
1. Paid advertising: Advertisers pay to spread their message through media outlets such as television, radio, print, billboards, online, and social media.
2. Impersonal Communication: Advertising is a form of mass communication that reaches many people at once without targeting a specific individual. Advertising clarifies which company, brand, or group is pushing the product, service, or idea.
3. Persuasion: The primary purpose of advertising is to convince or influence the target audience to take a desired action, such as buying a product, using a service, or an opinion, or adopting a particular conduct.
4. Use of Creative Techniques: Advertisements usually incorporate creative techniques such as catchy images, persuasive words, memorable jingles, and emotional appeal to attract the audience’s mind and effectively convey the desired message.
5. Demographic targeting: Effective advertising efforts are designed for specific target audiences based on demographics, mood, location, and consumer behaviorWhat is an Advertising Agency?
Promotional firms provide businesses and organizations with a variety of marketing and promotion services. Furthermore, they serve as go-betweens for customers and other media companies
Some of the key services offered by advertising agencies include the following: maintaining social media accounts, purchasing and scheduling media, creating creative material (such as copywriting, graphic design, and video production), creating branding strategies, and doing market research.
An advertising firm’s talented personnel includes artists, data analysts, media planners, account managers, and creative directors. Prior to initiating a multi-channel advertising campaign spanning several media platforms, such as print, web, television, outdoor, and social media, clients are consulted carefully to understand their marketing goals, target demographic, and available budget.
Advertising companies often ask their customers to compensate them for their knowledge and services. Ad agencies that are highly esteemed worldwide include Omnicom, Publicis Group, WPP, and Interpublic Group. By raising brand visibility, consumer engagement, and income, their advertising efforts ultimately aim to assist their clients in growing their businesses.